In the natural microflora of humans and animals, pathogenic fungi are not present. Fungi are eukaryotes that lack chlorophyll and are unable to perform photosynthesis. A large number of fungi are environmental saprophytes (heterotrophs) and need to be fed with ready -made organic matter. The fungal body is represented by the mycelium - a network of thinly branched tubular filaments called hyphae. The fungus reproduces by spores. Entering susceptible host tissues during inadvertent inoculation, in its good nutrient substrate, the fungus can cause a variety of diseases on the skin, mucous membranes, and internal organs. Fungal diseases are called mycoses (from the Greek. Mykes - fungus).
The causative agents of mycosis are microscopic parasitic fungi of the genus: Arthroderma, Aspergillus, Amanita, Microsporum, Penicillium, Candida, Saccharomyces, Trichophyton, Epidermophyton, etc. Systemic mycoses of internal organs are very difficult and can affect, in addition to the skin, muscles, bones, internal organs and nervous system. Actinomycosis is a serious disease caused by the radiant fungus actinomycetes, blastomycosis is a deep skin mycosis, the causative agent is a pathogenic dimorphic fungus. Other diseases are also included in deep (visceral) mycoses. Superficial mycoses affect the stratum corneum, scalp, nail plate and mucous membranes.
The most common keratomycosis, which affects only the stratum corneum; dermatomycoses affect the smooth skin, epidermis and its complement: hair, nails.
Depending on the type of pathogenic fungus and the localization of the pathological process, there are:
- epidermophytosis - skin mycoses of the inguinal folds, lower limbs, interdigital folds, brush;
- tricomycosis (from the Greek trichos - hair) - damage to the scalp, vellus hair on the body;
- trichophytosis (ringworm), microsporia, favus (scabies);
- onychomycosis (from the Greek onychos - nails) - damage to the nail plates on the hands or feet with dermatophytes (more rarely mold or yeast).
For diseases caused by various types of pathogenic or opportunistic fungi, antifungal drugs are used. Depending on the localization of the pathogenic fungus, antifungal drugs are classified as drugs for treatment:
- systemic mycoses;
- candidiasis;
- superficial mycoses.
The chemical classification divides antifungal drugs into:
antibiotics:
- polyene antibiotics (amphotericin B, amphoglucamine, natamycin, nystatin);
- non -polyene antibiotics (griseofulvin);
synthetic medicine:
- imidazole derivatives (bifonazole, isoconazole, ketoconazole, clotrimazole, miconazole, oxyconazole, omoconazole, sertaconazole);
- triazole derivatives (itraconazole, fluconazole, thermoconazole, thioconazole);
- allylamine derivatives (terbinafine, naftifine);
- morphine derivatives (amorolphins);
- derivatives of different chemical groups: ciclopirox undecylenic acid, flucytosine, potassium iodide, etc.
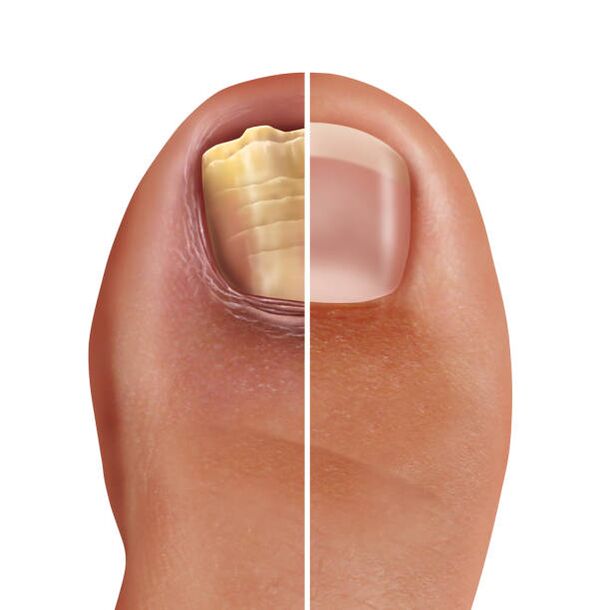
Onychomycosis
Onychomycosis is caused by an infection of the nail plate. A large number of infections occur in public baths, saunas, swimming pools. Scales, which contain fungal spores and mycelium, fall on patients with onychomycosis, falling on floors, benches, trellis, streets, carpets and beds. In conditions of high humidity, the fungus can not only survive for a long time (many years), but also multiply, which makes it a strong source of infection. A person who moves on the floor barefoot or touches household items with such scales may become infected, as they stick to his skin and are repaired. The infection develops after the penetration of the fungus into the nail structure. In the future, they begin to activate, multiply and form tunnels, quotes. When exposed, the nails thicken, crumble, turn yellow and break. Sometimes this process also affects the skin, which is accompanied by an itchy rash and flaking in the interdigital area. Such diseases are distinguished by a long and continuous journey.
The likelihood of susceptibility to infection increases with age, especially in the elderly over 65 years, due to the presence of chronic diseases such as vegetative-vascular pathology, diabetes mellitus, peripheral circulatory disorders, osteoarthropathy of the legs, and others. nail plate.
Treatment of onychomycosis is carried out strictly according to a specific scheme for a long time - from 2 to 4 months. In therapy, antimycotics are used, which have fungistatic and fungicidal effects and affect various stages of vital activity and metabolism of pathogens. There are three main mechanisms of antimycotic action of antifungal drugs, which show their activity as a result:
- violation of the structure and function of the fungal cell wall (imidazole, triazole);
- violation of eukaryotic cell mitosis, by inhibiting the synthesis of nucleic acids (griseofulvin);
- inhibition of transmembrane exchange processes through fungal cell membranes (ciclopirox).
The drug of choice
GriseofulvinTab (Griseofulvinum). 125 mg is an antibiotic produced by the mold Penicillium nigricans (griseofulvum), isolated in 1939 and is a spiro derivative of benzofuran in structure. The drug has fungistatic properties against all types of fungi - trichophytes and epidermophytes. The mechanism of fungistatic action is based on the ability of the drug to inhibit cell division from filamentous fungi in metaphase, cause characteristic morphological changes (twisting, increased branching and hiphae curvature), disrupt mitotic spindle structure and cell wall synthesis. To a small extent, these drugs inhibit the synthesis and polymerization of nucleic acids. This drug has no antibacterial activity.
To create a sufficient concentration of the drug on the skin requires long -term treatment - 2-3 months min. Only on new and regrowth nails, the first symptoms of the effectiveness of the treatment can be seen.
Important! Side effects while taking the drug include: dyspeptic disorders, dizziness, sometimes insomnia, allergic reactions, leukopenia. Griseofulvin is contraindicated in suppression of hematopoiesis, liver and kidney failure, as well as in infants and pregnant women. You should not give medication to transport drivers, people who are engaged in work with high altitude or require attention, mental and motor reactions quickly. Patients should be warned about the possible development of cross -sensitivity to penicillin and about the increased effects of alcohol.
Ketoconazole(Ketoconazole) - an active broad -spectrum drug from the imidazole group with fungicidal and fungistatic activity; effective when taken orally with systemic and superficial mycosis, dermatomycosis and candidiasis. It is prescribed by doctors for the treatment and prevention of fungal infections on the skin, hair, nails, genitals caused by pathogens that are sensitive to the drug.
When given orally, the drug is well absorbed, dissolved and absorbed in an acidic environment.
Important! The drug is well tolerated by patients, but can cause dyspeptic symptoms (nausea, vomiting, diarrhea), very rarely there are allergic reactions in the form of urticaria and skin rashes, headache, dizziness, gynecomastia, impotence. With the simultaneous use of the drug with other drugs (fentanyl, tamsulosin, carbamazepine, salmeterol, etc. ), the concentration of the latter may increase with increasing side effects.
Contraindications to the liver, kidneys, pregnancy, lactation and severe hypersensitivity to the drug.
Ketoconazole is available in the table. 200 mg suppository. 400 mg; Ointment 2%, 15 mg; cream 20 mg / g - 15 g. It is used in the form of shampoo. The duration of treatment is determined individually.
Itraconazole(Itraconazolum) topi. 100 mg; solution of 10 mg / ml - bottle150 ml - the drug has a broad spectrum of action, selectively and specifically inhibits enzymes that catalyze the synthesis of fungal sterols. Scope: various infections caused by dermatophytes and / or fungi and fungal fungi, such as mucous membrane candidiasis (including vaginal), skin mycoses, onychomycosis, epidermomycosis, fungal lesions of the eye (keratitis), peritoneum and other localizations. Taking Itraconazole capsules immediately after a meal increases bioavailability; maximum concentration in blood plasma is reached in 3-4 hours. after ingestion. The drug is well distributed in tissues prone to fungal infections.
Important! While using the drug, side effects from the digestive system may occur: dyspepsia (nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation, loss of appetite), abdominal pain, discomfort; headache, dizziness, allergic reactions, alopecia, from hematopoietic organs (rare) - leukopenia, thrombocytopenia. Its use is contraindicated in case of hypersensitivity to itraconazole and any component of the drug, children under 3 years of age, pregnancy and lactation.
For optimal absorption of the drug, it is necessary to take the capsule without chewing, immediately after eating, swallow whole. A course of pulse therapy for onychomycosis consists of taking 2 caps daily. medication twice a day for a week. For the treatment of fungal infections on nail plates, two courses are recommended. For the treatment of fungal infections on the nail plates on the feet, three courses are recommended. The interval between courses, during which you do not have to take medication, is 3 weeks.
Terbinafine(Terbinafine) - produced in the form of: tab. 250 mg; Ointment 1% 15. 0 g; 1% cream - tubes of 10, 15, 30 g; 1% spray, 20 ml. These drugs are referred to as allylamines and are prescribed for systemic and external use. Mechanism of action Terbinafine is associated with inhibition of the early stages of ergosterol biosynthesis (the major cell sterol of fungal membranes) by inhibiting the specific enzyme squalene-2, 3-epoxidase on fungal membranes. The drug is effective against many fungal pathogens in humans. With topical treatment, Terbinafine is more effective than azole drugs, imidazole derivatives, but comparable to itraconazole, and when given orally, it is more effective than griseofulvin and itraconazole. Terbinafine is characterized by lipoidophilicity, rapidly permeates into the stratum corneum of the epidermis, dermis, subcutaneous tissue, accumulates in the sebaceous glands, hair follicles and nail plates in concentrations that exert a fungicide effect. 1 tab. terbinafine once daily resulted in higher cure rates and better outcomes for each efficacy criteria (including mycological cures) than intermittent intraconazole therapy.
Naftifin(Naftifine) cream 1% - 15, 30 g; 1% solution of 10, 20, 30 ml, is a derivative of allylamines. The mechanism of action is associated with inhibition of the activity of the enzymes squalene-2, 3-epoxidase, inhibition of ergosterol biosynthesis, which leads to a violation of cell wall synthesis. Naftifine has a broad spectrum of action, acting as a fungicide against dermatophytes (such as Trichophyton, Epidermophyton, Microsporum), molds (Aspergillus spp. ), Yeast -like fungi (Candida spp. , Pityrosporum) and other fungi, for example (Sphenor scorotrichosis). . . This drug has anti-inflammatory effect, reduces itching. When applied externally, it penetrates the skin well, creating a stable antifungal concentration in its various layers.
The duration of treatment with Naftifin varies from 2 weeks to 6 months. While using the drug, dryness and redness on the skin, a burning sensation may occur, all these side effects are reversible and do not require cancellation.
Amorolfine(Amorolfine) nail polish 5% - 2, 5 and 5 ml, - preparation for external use, has a broad spectrum of action, provides fungistatic and fungicidal action due to damage to the fungal cytoplasm membrane by interfering with sterol biosynthesis, due to inhibition of the enzyme 14– gamma demethylaseand 7 gamma isomerase. The drug is active against the most common and rare dermatophyte nail fungal infection pathogen: Trichophyton spp. , Microsporum spp. , Epidermophyton spp. ; reference: Alternaria spp. , Scopulariopsis spp. , Hendersonula sppi. ; fungi of the Dematiaceae family: Cladopsorium spp. , Fonsecaea spp. , Wangiella spp. ; dimorphic fungi Coccidioides spp. , Histoplasma spp. , Sporothrix spp.
When applied to the nail, the drug penetrates into the nail plate and subsequently into the nail bed, almost completely in the first 24 hours. The effective concentration remains on the affected nail plate for 7-10 days. after the first application. Systemic absorption is negligible. It is used externally. The drug is applied to damaged fingers or toenails 1-2 times a week. The duration of treatment is determined individually and depends on the indications for use. Side effects are rare and appear in the form of itching, burning at the site of application. Not prescribed for children and small babies.
Undecylenic acidand its salts - antifungal drugs for external use, which have fungistatic and fungicide effects on dermatophytes, when combined with zinc or copper salts - zinc undecylenate or copper undecylenate - increased activity. Zinc, which is part of the drug, has an astringent effect, reduces the manifestation of signs of skin irritation and promotes faster healing.
- Undecylenic acid + zinc undecylenate (TN, ointment 30 g tube, ointment 25 g in a bottle);
- Undecylenic acid + Copper undecylenate + HCV glycerol - used to treat and prevent fungal skin diseases caused by drug -sensitive fungi (dermatophytes).
The preparation is applied on a clean and dry surface on the affected skin 2 times a day (morning and evening). The duration of treatment is 4-6 weeks and depends on the nature, effectiveness and course of the disease. After the disappearance of clinical signs of the disease, they continue to be used once a day. For preventive purposes - 2 times a week.
Important! Contraindications to the use of such drugs are hypersensitivity to undecylenic acid and its derivatives.
Cyclopirox(Ciclopirox) nail polish 8%, fl. 3 g, is a broad -spectrum antifungal drug that inhibits the capture of precursors for macromolecular synthesis in cell membranes. Applied externally for the treatment and prevention of fungal infections of the skin, mucous membranes, nails, fungal vaginitis and vulvovaginitis.
The drug is applied 1-2 times a day on the affected nails, the duration of its use depends on the severity of the lesion, but should not exceed 6 months.
Treatment of onychomycosis should be performed under the close supervision of a dermatologist. As a rule, rational etiotropic complex therapy is used. A decrease or disappearance of clinical symptoms is usually observed a few days after taking antimycotics. However, to prevent the disease from recurring, the course of treatment should be done in full. Against the background of clinical healing, anti-relapse therapy is often performed, aimed at preventing re-infection.















